Tesla Model S/X A/C Compressor: Difference between revisions
Jason arnold (talk | contribs) First draft of page with placeholders for future content. |
Categories |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
There are two known variants of A/C compressors used in Model S & X. The first generation is a unit by Denso which can be controlled via PWM. Later units built by HVCC and Hanon are CAN-controlled | [[File:Early-Tesla-airconditioning-compressor.png|thumb|300x300px|Tesla gen 1 A/C compressor|link=Special:FilePath/Early-Tesla-airconditioning-compressor.png]] | ||
There are two known variants of A/C compressors used in Model S & X. The first generation is a unit by Denso which can be controlled via PWM. Later units built by HVCC and Hanon are CAN-controlled. This page deals with gen 1 units, details for controlling the gen 2 CAN variants are found [[Tesla Model S/X A/C Compressor Gen2|here]]. | |||
Early years of Model S (2013-2014) used an ES34C by Denso with part number 6007380-00-D. | |||
Later models (2015+) used a HVCC ESC33 with Tesla part number 1028398-00-E, 1028398-00-F and 1028398-00-J. Tesla also used the Hanon HES33 and is found with number 1063369-00-D, 1063369-00-E, 1063369-00-F and 1063369-00-G. | |||
== | ==Gen 1 Unit (Denso ES34C)== | ||
=== | === Power Draw === | ||
As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1061852 | |||
==== LV ==== | ''Current draw at maximum load is in the neighbourhood of 12 amps @ 360V, so somewhere around 4.5kW draw.'' | ||
===Control/Pinouts=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="float:right; margin-left: 10px;" | |||
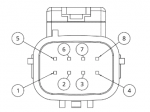
|+LV pinout | |||
[[File:Connector-Tesla-AC-compressor.png|link=link=Special:FilePath/Connector-Tesla-AC-compressor.png|frameless|150x150px]]<small>(compressor view)</small> | |||
!pin | |||
!function | |||
|- | |||
|1 | |||
|GND | |||
|- | |||
|2 | |||
|On/Off | |||
|- | |||
|3 | |||
|Diagnostics | |||
|- | |||
|4 | |||
|''Not connected'' | |||
|- | |||
|5 | |||
|Power feedback | |||
|- | |||
|6 | |||
|PWM in | |||
|- | |||
|7 | |||
|12V in | |||
|- | |||
|8 | |||
|''Not connected'' | |||
|} | |||
As mentioned above, the Denso ES34C can be controlled using a PWM signal. | |||
As per: https://www.evcreate.nl/using-tesla-thermal-management-system-parts/#tesla-ac-compressor | |||
''Connect 12V + in to pin 7 and provide chassis ground to pin 1. Pin 4 and 8 are not connected (don’t even have a male terminal in the compressor connector). You can leave the power feedback (pin 5) and diagnostics (pin 3) unconnected too.'' | |||
''The compressor is enabled by grouding pin 2 (active low) and speed control via a PWM signal on pin 6.'' | |||
As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1029299 | |||
''Success! I got the ES34C running. It is very easy to control and very tolerant of input conditions. It takes a PWM signal anywhere from 35 to 400 hz. Control range is from 5% (max speed) to 85% (min speed) duty cycle.'' | |||
''I supplied 12V to Pin 7 (VIgn), Grounded pins 1 (Gnd) and 2 (On/Off), and left pins 3 (Diag) and 5 (Power (FB)) unconnected. The 12V PWM signal was input to pin 6 (PWMin).'' | |||
===Wiring/Connectors=== | |||
====HV==== | |||
Polarity of the HV connector (as looking into the connector): | |||
[[File:Denso-ES34C-HV-polarity.jpg|border|200x200px]] | |||
Details of the connector itself are currently unknown, though an HV cable from a Lexus hybrid (i.e. GS450H) A/C compressor has been known to work if a Tesla assembly can't be sourced. | |||
====LV==== | |||
As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1062935 | |||
''Female connector for control signals is Sumitomo P/N: 6189-1240'' | |||
[[File:8pin-Female-Sealed-Auto-Wire-6189-1240-Sumitomo-Connector.jpg|alt=|border|200x200px]] | |||
=== Controller === | |||
An Arduino MEGA-based controller has been developed by DIYEC user ''Classic Style''. Details here: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1067794 | |||
=== Integration with aftermarket HVAC === | |||
It has been pointed out that a typical HVAC trinary switch will provide a 12V signal to enable (might be typical on ICE compressors), however, in this case the Denso ES34C is looking for a GND signal to enable (pin 2 - ON/OFF). As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1075637, DIYEC users ''jsimonkeller'' and ''DANTM'' managed this simply by using a typical automotive relay to invert the signal and switch GND instead of 12V. | |||
[[Category:Tesla]] | |||
[[Category:AC Compressor]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:18, 20 December 2024
Overview

There are two known variants of A/C compressors used in Model S & X. The first generation is a unit by Denso which can be controlled via PWM. Later units built by HVCC and Hanon are CAN-controlled. This page deals with gen 1 units, details for controlling the gen 2 CAN variants are found here.
Early years of Model S (2013-2014) used an ES34C by Denso with part number 6007380-00-D.
Later models (2015+) used a HVCC ESC33 with Tesla part number 1028398-00-E, 1028398-00-F and 1028398-00-J. Tesla also used the Hanon HES33 and is found with number 1063369-00-D, 1063369-00-E, 1063369-00-F and 1063369-00-G.
Gen 1 Unit (Denso ES34C)
Power Draw
As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1061852
Current draw at maximum load is in the neighbourhood of 12 amps @ 360V, so somewhere around 4.5kW draw.
Control/Pinouts
| pin | function |
|---|---|
| 1 | GND |
| 2 | On/Off |
| 3 | Diagnostics |
| 4 | Not connected |
| 5 | Power feedback |
| 6 | PWM in |
| 7 | 12V in |
| 8 | Not connected |
As mentioned above, the Denso ES34C can be controlled using a PWM signal.
As per: https://www.evcreate.nl/using-tesla-thermal-management-system-parts/#tesla-ac-compressor
Connect 12V + in to pin 7 and provide chassis ground to pin 1. Pin 4 and 8 are not connected (don’t even have a male terminal in the compressor connector). You can leave the power feedback (pin 5) and diagnostics (pin 3) unconnected too.
The compressor is enabled by grouding pin 2 (active low) and speed control via a PWM signal on pin 6.
As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1029299
Success! I got the ES34C running. It is very easy to control and very tolerant of input conditions. It takes a PWM signal anywhere from 35 to 400 hz. Control range is from 5% (max speed) to 85% (min speed) duty cycle.
I supplied 12V to Pin 7 (VIgn), Grounded pins 1 (Gnd) and 2 (On/Off), and left pins 3 (Diag) and 5 (Power (FB)) unconnected. The 12V PWM signal was input to pin 6 (PWMin).
Wiring/Connectors
HV
Polarity of the HV connector (as looking into the connector):
Details of the connector itself are currently unknown, though an HV cable from a Lexus hybrid (i.e. GS450H) A/C compressor has been known to work if a Tesla assembly can't be sourced.
LV
As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1062935
Female connector for control signals is Sumitomo P/N: 6189-1240
Controller
An Arduino MEGA-based controller has been developed by DIYEC user Classic Style. Details here: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1067794
Integration with aftermarket HVAC
It has been pointed out that a typical HVAC trinary switch will provide a 12V signal to enable (might be typical on ICE compressors), however, in this case the Denso ES34C is looking for a GND signal to enable (pin 2 - ON/OFF). As per: https://www.diyelectriccar.com/threads/tesla-a-c-compressor-questions.189978/post-1075637, DIYEC users jsimonkeller and DANTM managed this simply by using a typical automotive relay to invert the signal and switch GND instead of 12V.